I am Kangning Liu, a Research Scientist at Adobe. I build large-scale vision and multimodal foundation models that bridge cutting-edge research with real-world industrial impact.
My current work focuses on advancing multimodal understanding and integrating powerful visual comprehension into generative models—enabling applications from GenAI data creation and reward modeling to AI agent tool calling. My research has been published at top-tier venues (NeurIPS, CVPR, ICCV, ICLR) and deployed in Adobe Photoshop, Lightroom, Express, and Firefly, reaching tens of millions of users.
I earned my Ph.D. at the NYU Center for Data Science, where I was advised by Prof. Carlos Fernandez Granda and Prof. Krzysztof J. Geras. Before that, I earned my M.Sc. in Data Science from ETH Zurich and my B.E. in Electrical Engineering from Tsinghua University.
Recent Updates
- Feb 2026: Our papers "VGent" and "Sparse-LaViDa" were accepted to CVPR 2026!
- Jan 2026: Our paper "LaViDa-O" was accepted to ICLR 2026!
- Dec 2025: "selectionByPrompt" feature shipped in Adobe Photoshop integrating into ChatGPT; served as research lead.
- July 2025: Our paper "RAS" was accepted to ICCV 2025!
For more details, feel free to reach out via email at kangning.liu[at]nyu.edu (still active). You can also find me on Google Scholar and LinkedIn .
Research Experience
-

Adobe
San Jose, California, USA (April 2024 - present)
Research Scientist II
- Multimodal Grounding & Reasoning: Enhance the grounding ability of multimodal large language models by integrating advanced reasoning capabilities and fine-grained understanding. These models enable a wide spectrum of applications, ranging from generative AI data creation and reward modeling for GenAI training to AI agent tool calling. For example, our "selectionByPrompt" feature [Adobe Blog] enables users to select content in an image using natural language with Adobe Photoshop in ChatGPT, and has since been integrated into AI Assistant in Photoshop for smarter image editing.
Related publications: VGent [CVPR 2026] RAS [ICCV 2025] - Unified Understanding & Generation: Working on unified frameworks that bring powerful visual comprehension—reasoning, grounding, and fine-grained perception—into generative models, enabling a single architecture to both understand and create visual content.
Related publications: LaViDa-O [ICLR 2026] Sparse-LaViDa [CVPR 2026] LaViDa-R1 [Preprint] - Vision Foundation Model: Developed cutting-edge segmentation foundation models to enhance Adobe products.
Contributions include core features deployed in Adobe Photoshop's newest selection tools [Media Review], remove background in Adobe Firefly [Feature Summary], and segmentation enhancements in Adobe Lightroom [Feature Summary] , Adobe Express.
Related publications: SUM [NeurIPS 2024] SVE [BMVC 2025] conSAMmé [CVPRW 2025]
- Multimodal Grounding & Reasoning: Enhance the grounding ability of multimodal large language models by integrating advanced reasoning capabilities and fine-grained understanding. These models enable a wide spectrum of applications, ranging from generative AI data creation and reward modeling for GenAI training to AI agent tool calling. For example, our "selectionByPrompt" feature [Adobe Blog] enables users to select content in an image using natural language with Adobe Photoshop in ChatGPT, and has since been integrated into AI Assistant in Photoshop for smarter image editing.
-

Adobe
San Jose, California, USA (May 2023 - Nov 2023)
Research Intern | Advisors: Dr. Brian Price, Dr. Jason Kuen, Dr. Yifei Fan, Dr. Zijun Wei, Luis Figueroa, Markus Woodson
- Foundation Model Development & Scale: Worked on segmentation foundation model research, processing millions of images via a model-in-the-loop data engine, potentially influencing the roadmap for features in Adobe products such as Photoshop and Lightroom.
- SOTA Performance & Quality Assurance: Achieved SOTA segmentation accuracy across 20+ test sets (5-point IoU: 0.869, surpassing SAM's 0.828). This work (SUM) was published in NeurIPS 2024 [Project Website] and established scalable feedback loops for iterative model refinement and product integration.
-

Google
Mountain View, California, USA (May 2022 - Sep 2022)
Research Intern | Advisors: Dr. Xuhui Jia, Dr. Yu-Chuan Su, Dr. Ruijin Cang
- One-shot Face Video Synthesis: Developed deep learning algorithms optimized for real-time one-shot face video synthesis, targeting efficient deployment on mobile devices.
- Quality & Control: Innovated a method enhancing geometric correspondence (7% in AKD) and overall quality (15% in AED), while incorporating a plug-in interface for flexible emotion manipulation.
-

Center for Data Science, New York University
New York, USA (Sept 2019 - March 2024)
Research Assistant | Advisors: Prof. Carlos Fernandez-Granda, Prof. Krzysztof J. Geras
- Robust Deep Learning with Noisy Labels: Engineered robust algorithms tailored for segmentation tasks, showing resilience against annotation noise. This ensures the model's reliability, especially in real-world scenarios where annotation noise is prevalent. This work (ADELE) was selected for CVPR 2022 Oral Presentation [GitHub].
- Weakly Supervised Learning: Proposed an innovative framework for multiple instance learning, which iteratively improves instance-level features by jointly estimating latent instance-level pseudo labels, and show that it outperforms existing methods on three real-world medical datasets. This work (ItS2CLR) was published in CVPR 2023 [GitHub].
- Video Understanding: Investigated and designed novel deep learning models for video action classification and segmentation, applied for the motion primitives prediction. This work (StrokeRehab) was published in NeurIPS 2022 [Paper Link].
-

Computer Vision Laboratory, ETH Zurich
Zurich, Switzerland (Oct 2018 - Aug 2019)
Research Assistant | Advisors: Prof. Luc Van Gool, Prof. Radu Timofte, Prof. Shuhang Gu
- Domain Adaptation: Improved cross-domain semantic segmentation methods for urban scene images through GAN models, harnessing weak paired information.
- Video and Image Synthesis: Achieved state-of-the-art performance in unsupervised multimodal video translation through bidirectional recurrent neural networks.
Publications
See also Google Scholar.
-
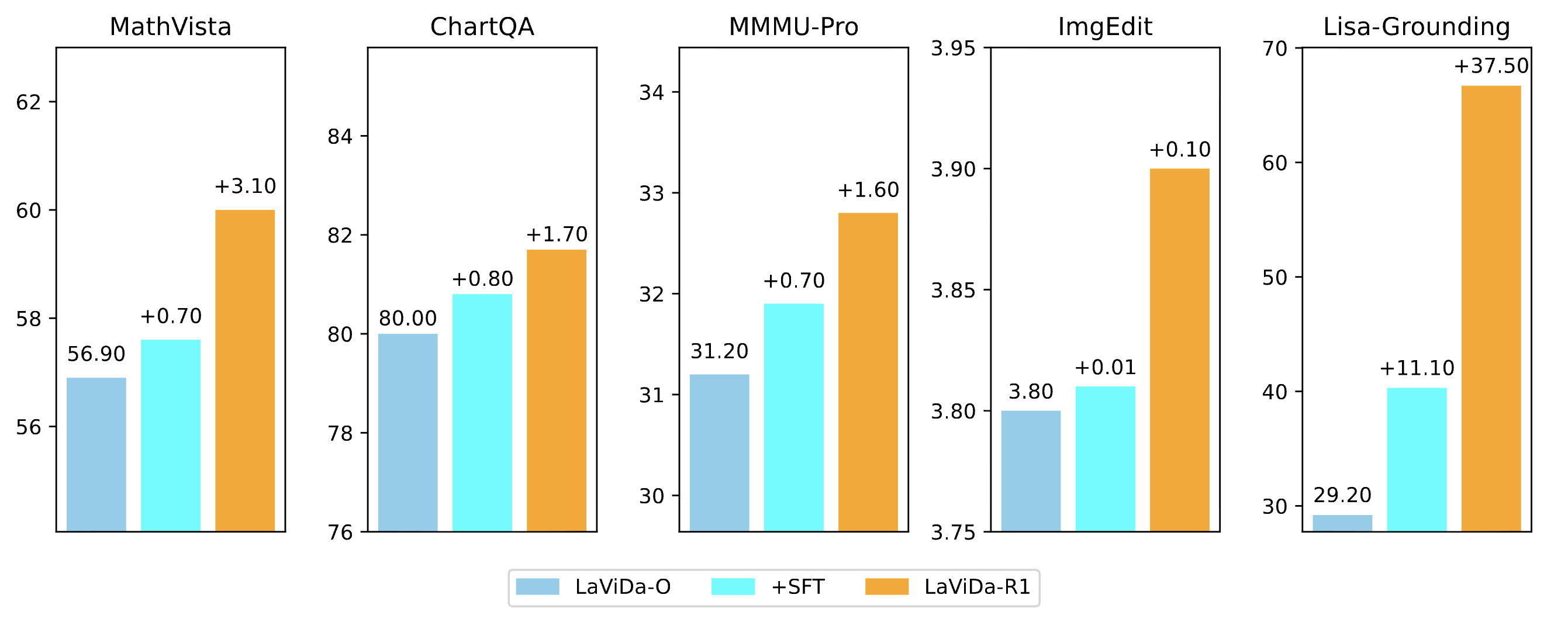
LaViDa-R1: Advancing Reasoning for Unified Multimodal Diffusion Language Models
Shufan Li, Yuchen Zhu, Jiuxiang Gu, Kangning Liu, Zhe Lin, Yongxin Chen, Molei Tao, Aditya Grover, Jason Kuen
Preprint
TL;DR: A unified reasoning diffusion language model combining supervised and reinforcement learning for multimodal understanding, generation, and editing.
Diffusion language models (dLLMs) recently emerged as a promising alternative to auto-regressive LLMs. The latest works further extended them to multimodal understanding and generation tasks. In this work, we propose LaViDa-R1, a multimodal, general-purpose reasoning dLLM. Unlike existing works that build reasoning dLLMs through task-specific reinforcement learning, LaViDa-R1 incorporates diverse multimodal understanding and generation tasks in a unified manner. In particular, LaViDa-R1 is built with a novel unified post-training framework that seamlessly integrates supervised finetuning (SFT) and multi-task reinforcement learning (RL). It employs several novel training techniques, including answer-forcing, tree search, and complementary likelihood estimation, to enhance effectiveness and scalability. Extensive experiments demonstrate LaViDa-R1's strong performance on a wide range of multimodal tasks, including visual math reasoning, reason-intensive grounding, and image editing.
-
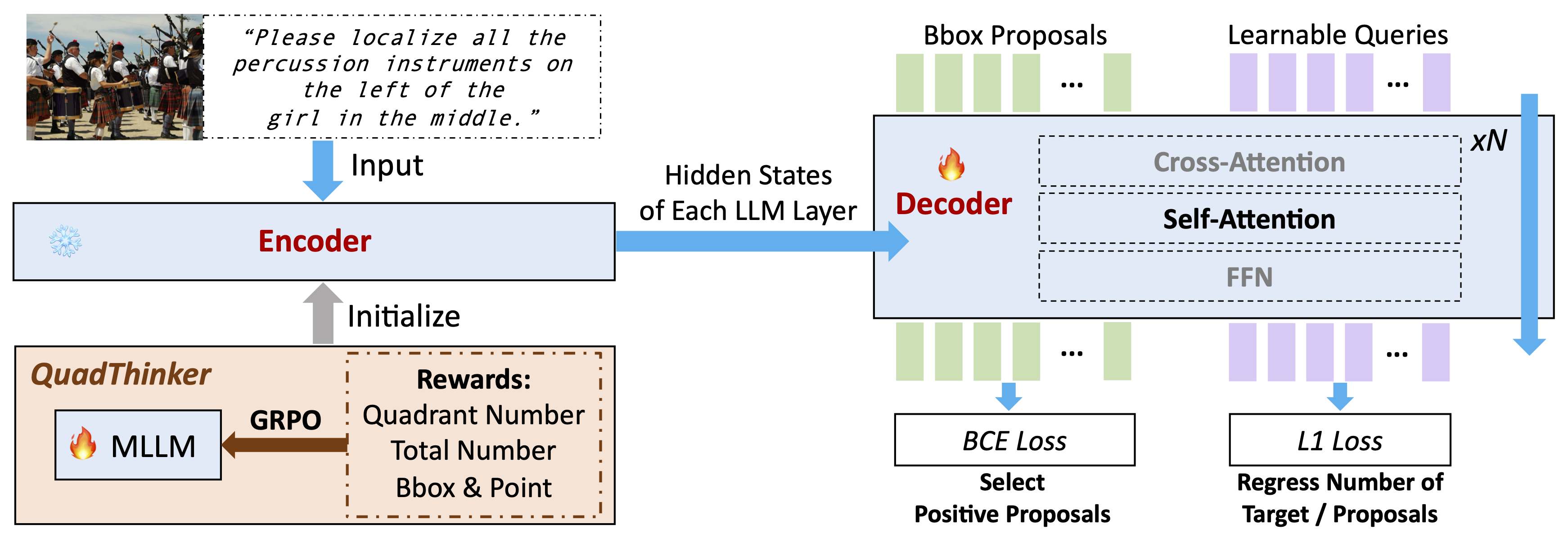
VGent: Visual Grounding via Modular Design for Disentangling Reasoning and Prediction
Weitai Kang, Jason Kuen, Mengwei Ren, Zijun Wei, Yan Yan, Kangning Liu*. (*project lead)
CVPR 2026
TL;DR: Modular architecture achieving +20% F1 in visual grounding by separating reasoning from prediction, enabling fast, accurate inference.
Current visual grounding models either rely on auto-regressive MLLMs (slow with hallucination risks) or re-align LLMs with vision features (potentially undermining reasoning). In contrast, we propose VGent, a modular encoder-decoder architecture that explicitly disentangles high-level reasoning and low-level bounding box prediction. A frozen MLLM serves as the encoder for powerful reasoning, while a decoder selects target box(es) from detector-proposed candidates via cross-attention on encoder hidden states. This design leverages advances in both object detection and MLLMs, avoids auto-regressive pitfalls, and enables fast inference. We introduce: (i) QuadThinker, an RL-based training paradigm for multi-target reasoning; (ii) mask-aware labels for resolving detection-segmentation ambiguity; and (iii) global target recognition to improve target identification. VGent achieves state-of-the-art performance with +20.6% F1 improvement, +8.2% gIoU, and +5.8% cIoU gains under visual reference challenges, while maintaining constant, fast inference.
-
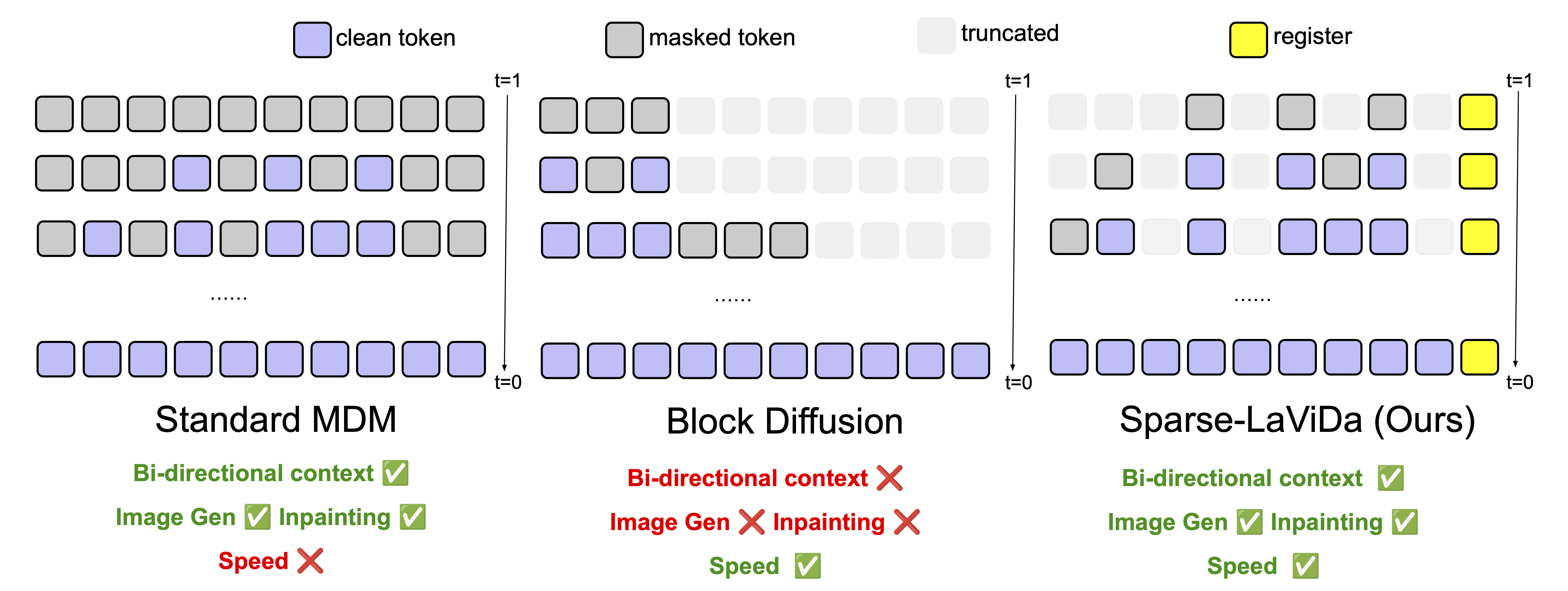
Sparse-LaViDa: Sparse Multimodal Discrete Diffusion Language Model
Shufan Li, Jiuxiang Gu, Kangning Liu, Zhe Lin, Zijun Wei, Aditya Grover, Jason Kuen.
CVPR 2026
TL;DR: Accelerates masked discrete diffusion dodels inference by dynamically truncates redundant masked tokens while preserving generation quality.
Masked Discrete Diffusion Models (MDMs) have achieved strong performance across a wide range of multimodal tasks, including image understanding, generation, and editing. However, their inference speed remains suboptimal due to the need to repeatedly process redundant masked tokens at every sampling step. In this work, we propose Sparse-LaViDa, a novel modeling framework that dynamically truncates unnecessary masked tokens at each inference step to accelerate MDM sampling. To preserve generation quality, we introduce specialized register tokens that serve as compact representations for the truncated tokens. Furthermore, to ensure consistency between training and inference, we design a specialized attention mask that faithfully matches the truncated sampling procedure during training.
-

LaViDa-O: Elastic Large Masked Diffusion Models for Unified Multimodal Understanding and Generation
Shufan Li, Jiuxiang Gu, Kangning Liu, Zhe Lin, Zijun Wei, Aditya Grover, Jason Kuen.
ICLR 2026
TL;DR: A single model unifying multimodal understanding and high-resolution (1024px) generation, outperforming both autoregressive and continuous diffusion approaches.
We propose LaViDa-O, a unified Masked Diffusion Model (MDM) that unifies multimodal understanding and high-resolution generation (1024px) within a single framework. By incorporating a novel Elastic Mixture-of-Transformers (Elastic-MoT) architecture, LaViDa-O couples a lightweight generation branch with a robust understanding branch, enabling efficient token compression and stratified sampling. The model further leverages planning and iterative self-reflection to boost generation quality. LaViDa-O achieves state-of-the-art performance across benchmarks for object grounding (RefCOCO), text-to-image generation (GenEval), and image editing (ImgEdit), outperforming leading autoregressive and continuous diffusion models while offering considerable inference speedups.
-
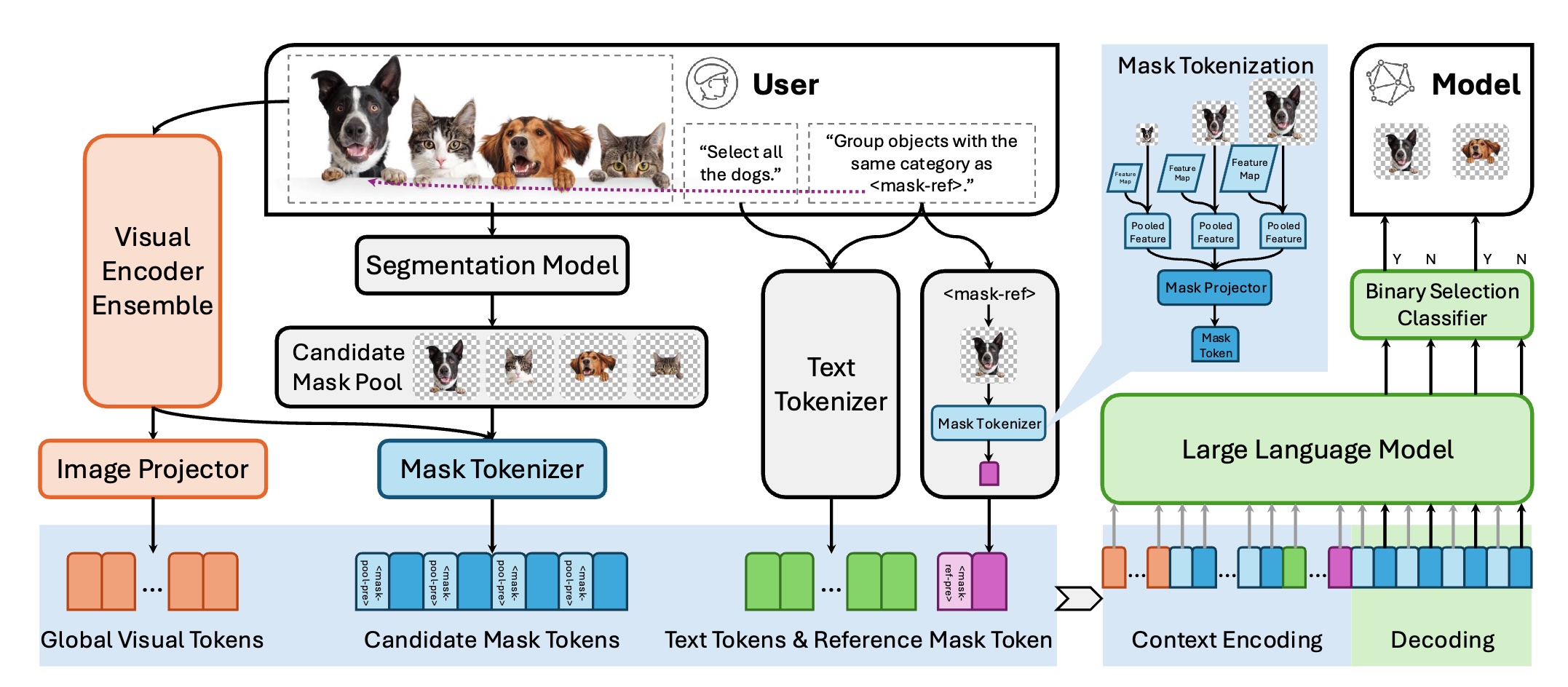
Refer to Any Segmentation Mask Group With Vision-Language Prompts
Shengcao Cao, Zijun Wei, Jason Kuen, Kangning Liu, Lingzhi Zhang, Jiuxiang Gu, HyunJoon Jung, Liang-Yan Gui, Yu-Xiong Wang
ICCV 2025
TL;DR: Enables referring to groups of segmentation masks via arbitrary text and visual prompts through a mask-centric multimodal model.
We introduce a novel task of omnimodal referring expression segmentation (ORES). In this task, a model produces a group of masks based on arbitrary prompts specified by text only or text plus reference visual entities. We propose a novel framework to "Refer to Any Segmentation Mask Group" (RAS), which augments segmentation models with complex multimodal interactions and comprehension via a mask-centric large multimodal model.
-
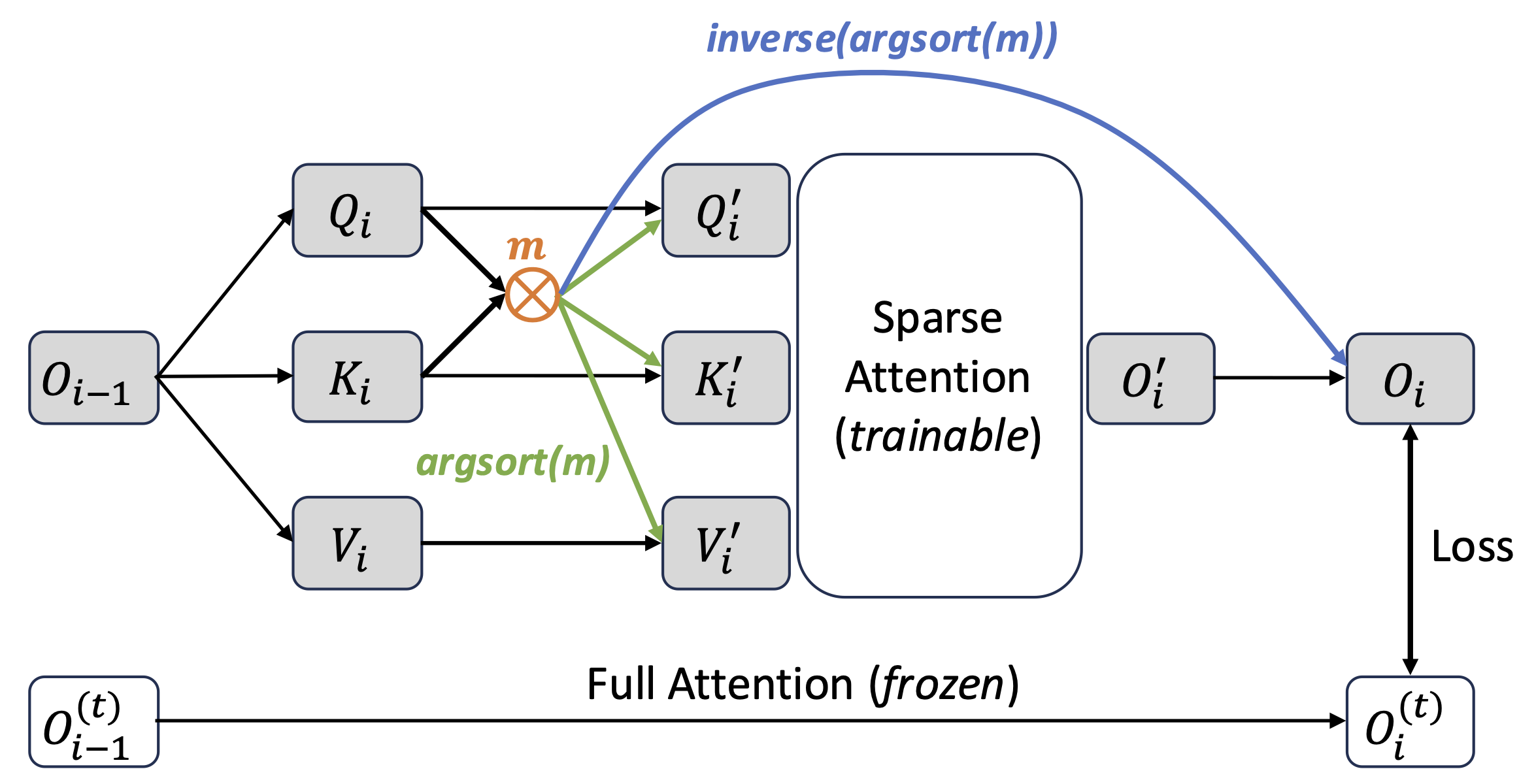
Leveraging Sparsity for Efficient Inference of High-Resolution Vision Foundation Models.
Xin Xu, Jason Kuen, Brian L. Price, Kangning Liu, Zijun Wei, Yu-Xiong Wang.
BMVC 2025
TL;DR: Up to 80% inference speedup for high-resolution vision encoders (DINOv2, CLIP, SAM2) by exploiting natural attention sparsity.
We introduce Sparse Vision Encoder (SVE), a post-training optimization framework that exploits naturally emerging sparsity in attention maps to accelerate inference of vision encoders. SVE selectively applies sparsity in key layers, performs sparsity distillation, and leverages cross-layer consistency to reuse sparsity structures. Experiments on DINOv2, CLIP, and SAM2 demonstrate up to 80% speedup for high-resolution encoding while preserving model performance.
-
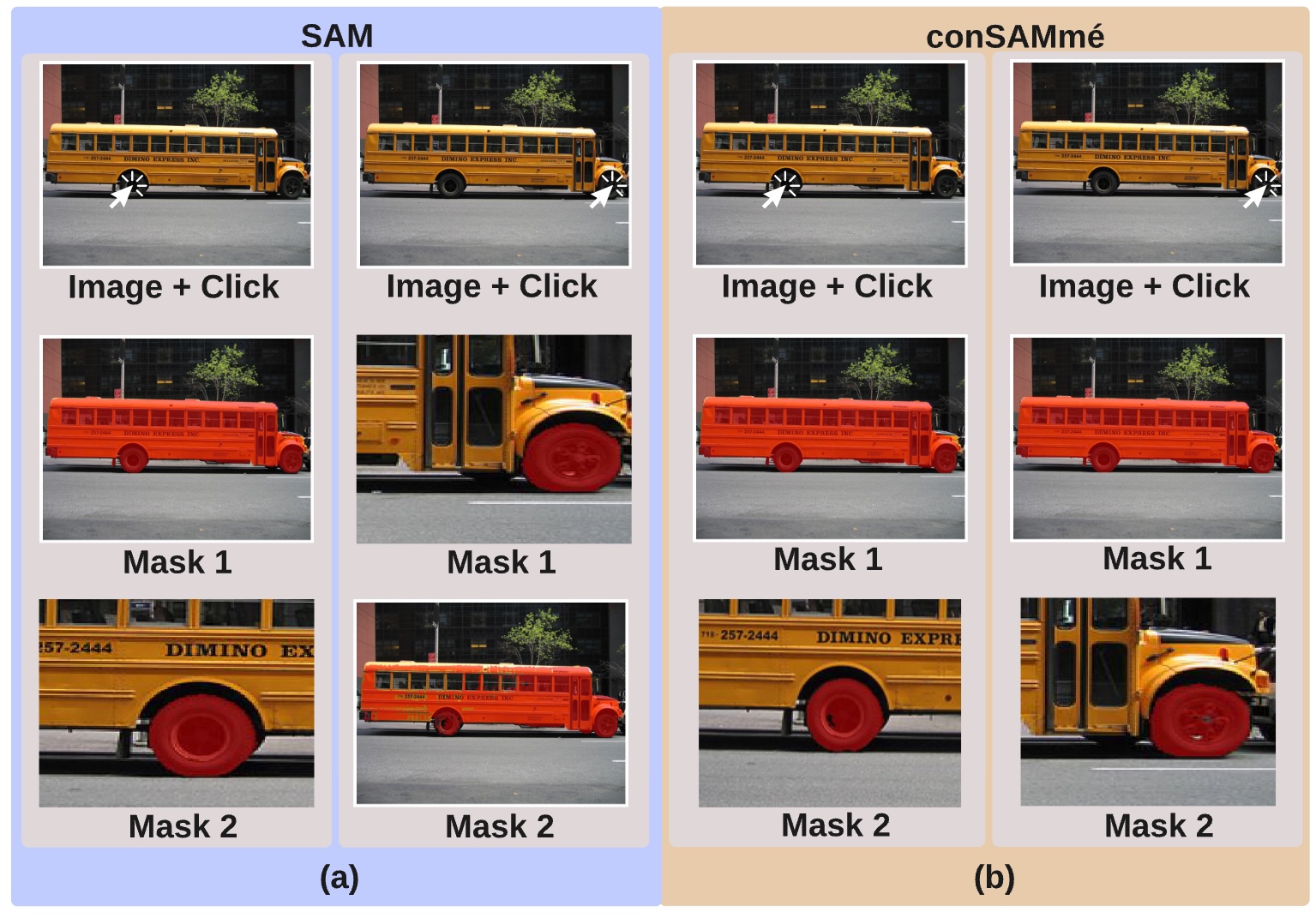
ConSAMmé: Achieving Consistent Segmentations with SAM
Josh Myers-Dean, Kangning Liu, Brian Price, Yifei Fan, Danna Gurari.
CVPRW 2025
TL;DR: Improves SAM’s segmentation consistency and mask ordering via contrastive learning with hierarchical semantics.
Multi-output interactive segmentation methods generate multiple binary masks when given user guidance, such as clicks. However, it is unpredictable whether the order of the masks will match or whether those masks will be the same when given slightly different user guidance. To address these issues, we propose conSAMme, a contrastive learning framework that conditions on explicit hierarchical semantics and leverages weakly supervised part segmentation data and a novel episodic click sampling strategy. Evaluation of conSAMme’s performance, click robustness, and mask ordering show substantial improvements to baselines with less than 1% extra training data compared to the amount of data used for the baseline.
-
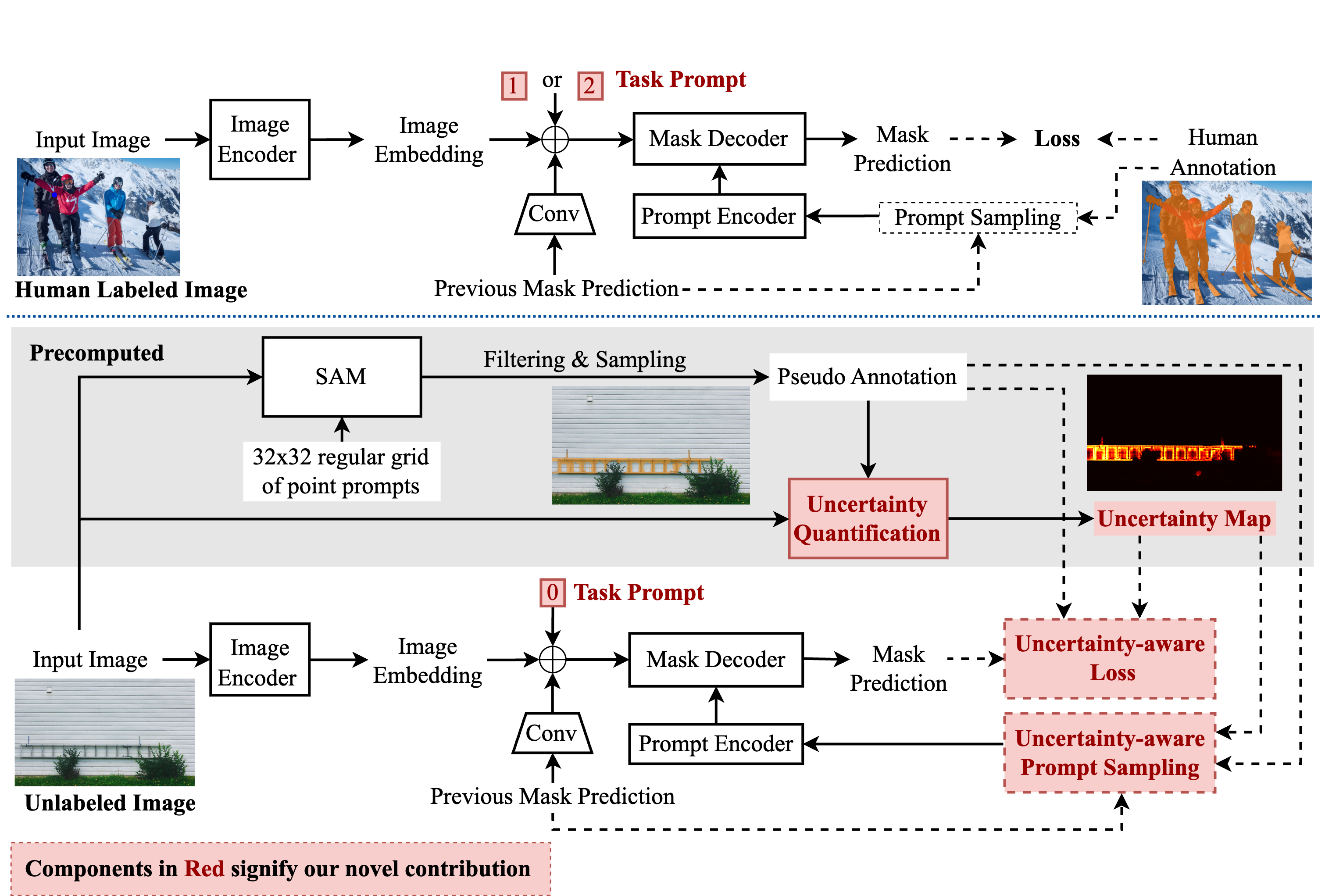
Uncertainty-aware Fine-tuning of Segmentation Foundation Models
Kangning Liu, Brian Price, Jason Kuen, Yifei Fan, Zijun Wei, Luis Figueroa, Krzysztof J. Geras, Carlos Fernandez-Granda.
NeurIPS 2024
TL;DR: Enhances SAM accuracy by 3-6 IoU points across 22 benchmarks through uncertainty-aware training and pseudo-label refinement.
The Segment Anything Model (SAM) is a large-scale foundation model that has revolutionized segmentation methodology. Despite its impressive generalization ability, the segmentation accuracy of SAM on images with intricate structures is unsatisfactory in many cases. We introduce the Segmentation with Uncertainty Model (SUM), which enhances the accuracy of segmentation foundation models by incorporating an uncertainty-aware training loss and prompt sampling based on the estimated uncertainty of pseudo-labels. We evaluated the proposed SUM on a diverse test set consisting of 22 public benchmarks, where it achieves state-of-the-art results. Notably, our method consistently surpasses SAM by 3-6 points in mean IoU and 4-7 in mean boundary IoU across point-prompt interactive segmentation rounds.
-
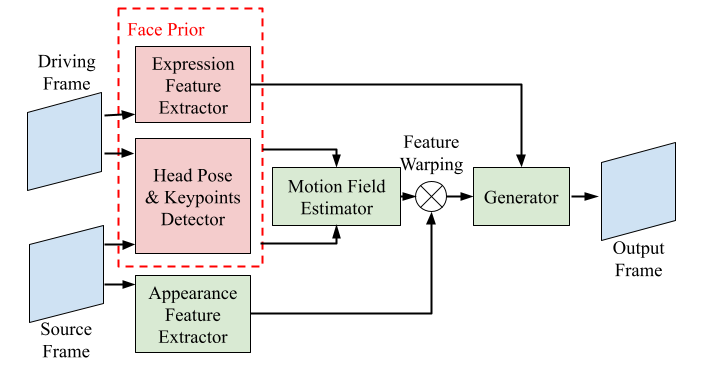
Controllable One-Shot Face Video Synthesis With Semantic Aware Prior
Kangning Liu, Yu-Chuan Su, Wei(Alex) Hong, Ruijin Cang, Xuhui Jia.
Preprint
TL;DR: Single-image face video generation with 7% better geometric accuracy and 15% better expression preservation, plus controllable emotion editing.
We propose a method that leverages rich face prior information to generate face videos with improved semantic consistency and expression preservation. Our model improves the baseline by 7% in average keypoint distance and outperforms the baseline by 15% in average emotion embedding distance, while also providing a convenient interface for highly controllable generation in terms of pose and expression.
-
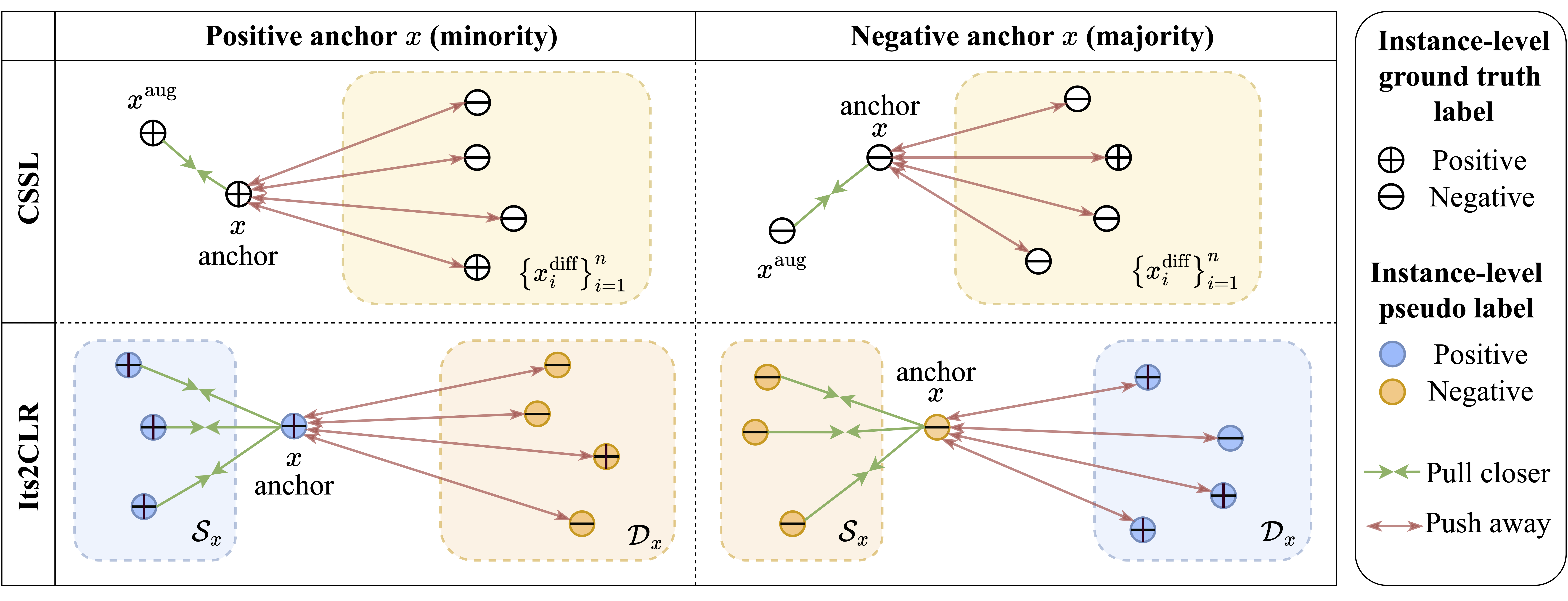
Multiple Instance Learning via Iterative Self-Paced Supervised Contrastive Learning
Kangning Liu*,Weicheng Zhu* (*Equal contribution), Yiqiu Shen, Sheng Liu, Narges Razavian, Krzysztof J. Geras, Carlos Fernandez-Granda.
CVPR 2023
TL;DR: Iterative contrastive learning framework improving instance-level classification in weakly-supervised settings.
In this paper, we introduce Iterative Self-Paced Supervised Contrastive Learning (Its2CLR), a novel method for learning high-quality instance-level representations in Multiple Instance Learning (MIL). Key features of our method: 1) self-paced learning to handle label noise and uncertainty; 2) supervised contrastive learning to learn discriminative instance-level embeddings; 3) iterative refinement of instance labels for robust and accurate classification.
-
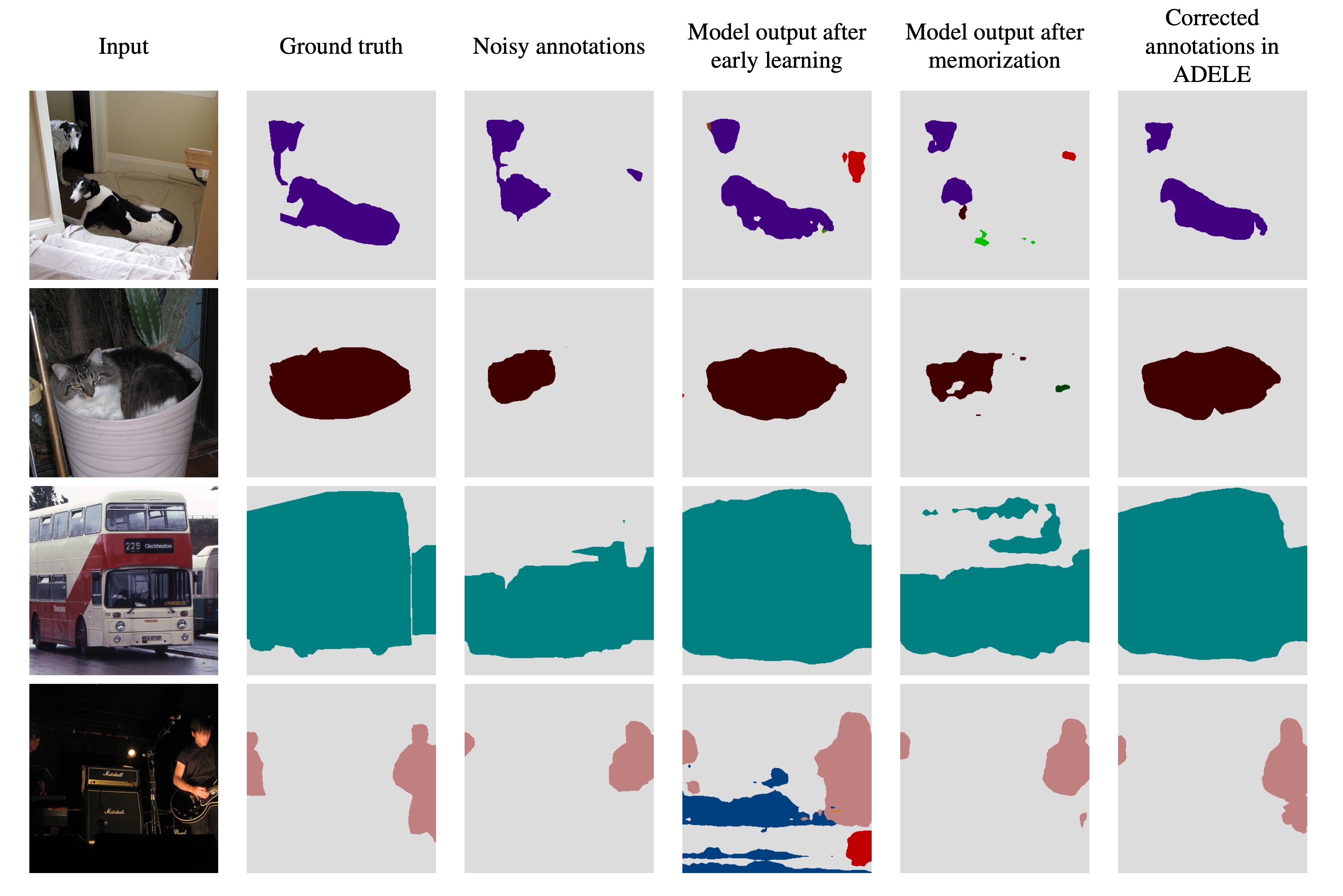
Adaptive early-learning correction for segmentation from noisy annotations
Sheng Liu*, Kangning Liu* (*Equal contribution, order decided by coin flip.), Weicheng Zhu, Yiqiu Shen, Carlos Fernandez-Granda.
CVPR 2022 Oral (4.2%)
TL;DR: Noise-robust segmentation that adaptively corrects noisy annotations during training — selected for Oral presentation (top 4.2%).
Deep learning in the presence of noisy annotations has been studied extensively in classification, but much less in segmentation tasks. In this project, we study the learning dynamics of deep segmentation networks trained on inaccurately-annotated data and propose a new method for semantic segmentation ADaptive Early-Learning corrEction (ADELE).
-
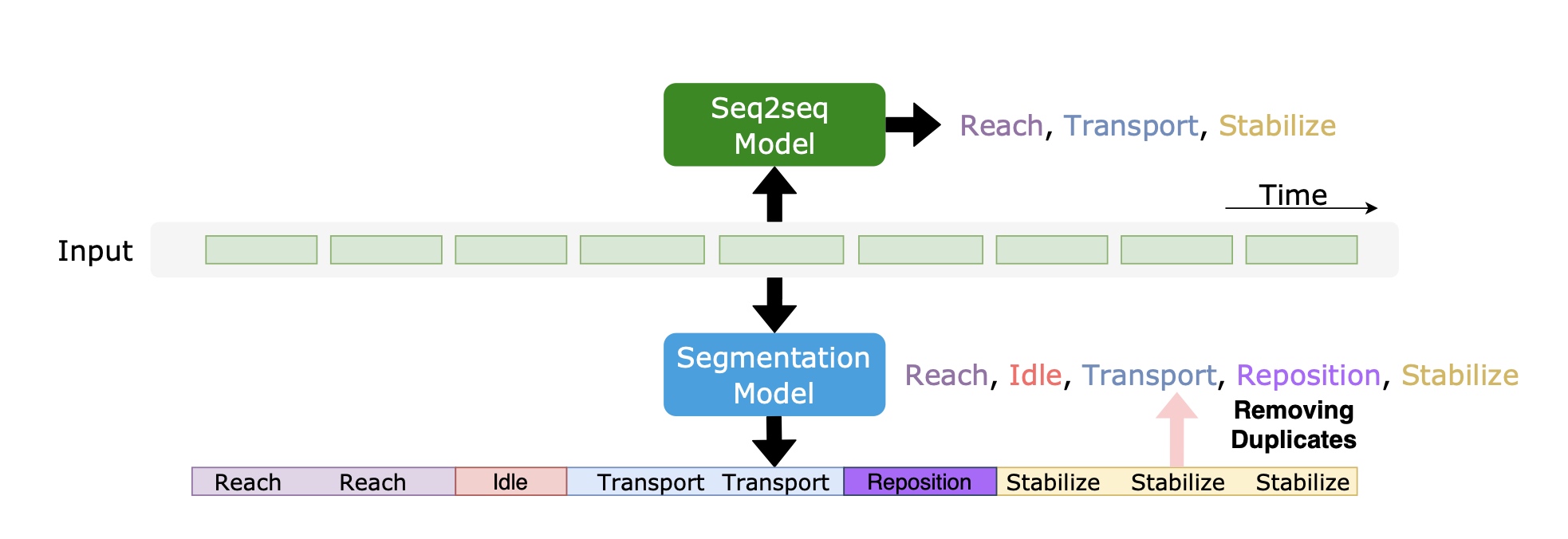
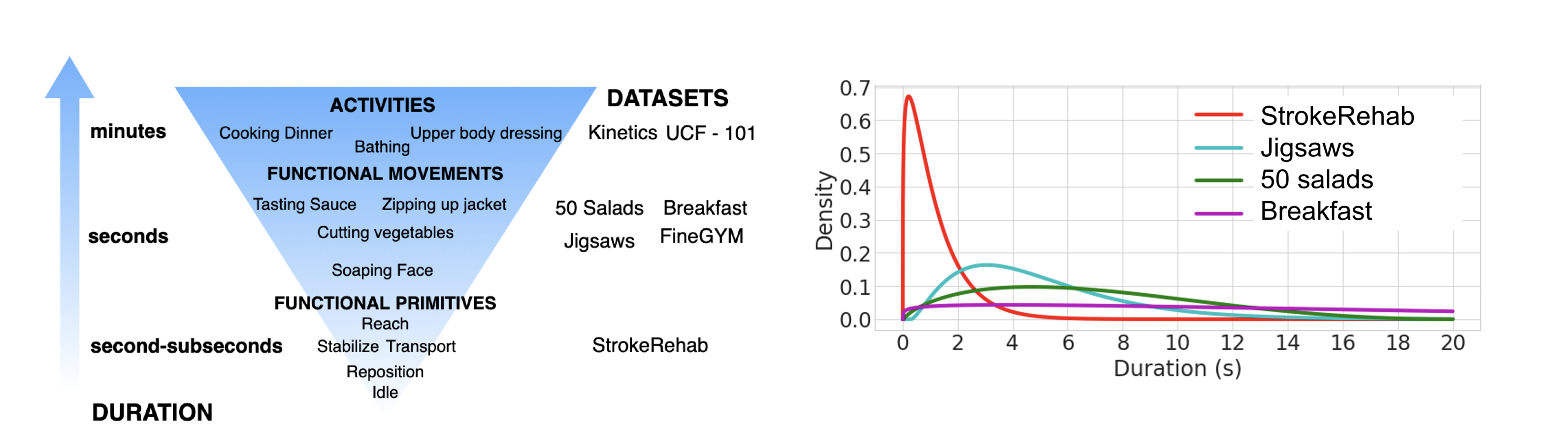
StrokeRehab: A Benchmark Dataset for Sub-second Action Identification
Aakash Kaku*, Kangning Liu* (*Equal contribution), Avinash Parnandi*, Haresh Rengaraj Rajamohan, Anita Venkatesan, Audre Wirtanen, Natasha Pandit, Kannan Venkataramanan, Heidi Schambra, Carlos Fernandez-Granda.
NeurIPS 2022
TL;DR: Benchmark and model for sub-second human action identification.
We introduce a new benchmark dataset for the identification of subtle and short-duration actions. We also propose a novel seq2seq approach, which outperforms the existing methods on the new as well as standard benchmark datasets.
-
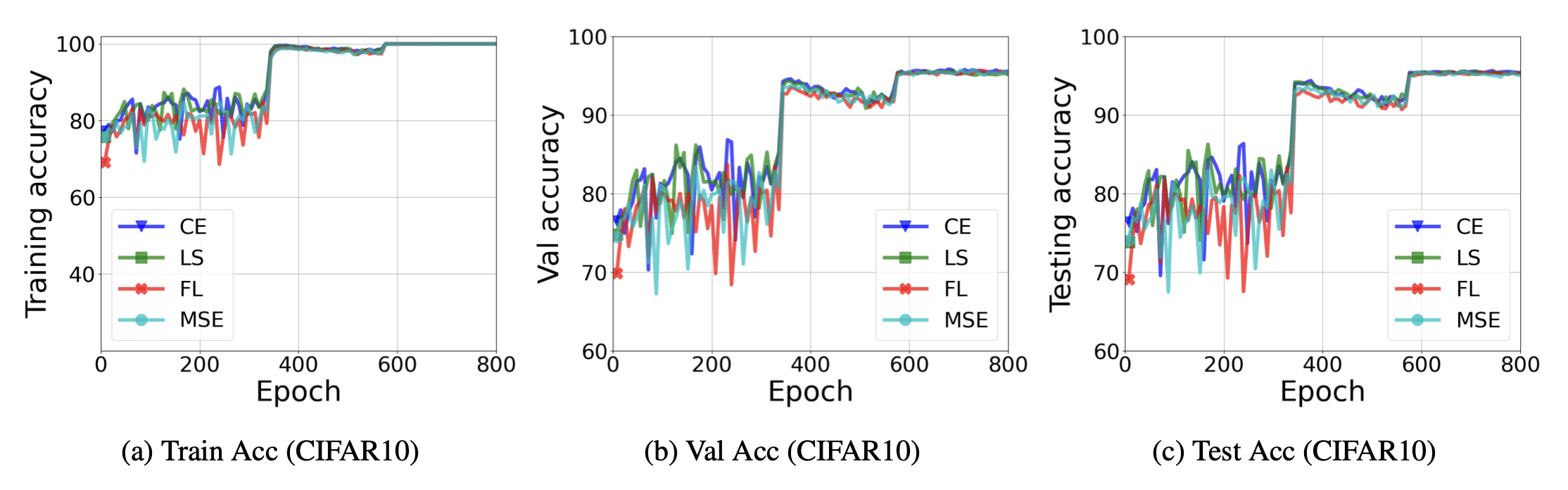
Are All Losses Created Equal: A Neural Collapse Perspective
Jinxin Zhou, Chong You, Xiao Li, Kangning Liu, Sheng Liu, Qing Qu, Zhihui Zhu.
NeurIPS 2022
TL;DR: Proves that a broad family of loss functions converge to neural collapse solutions with equivalent test performance.
A broad family of loss functions leads to neural collapse solutions hence are equivalent on training set; moreover, they exhibit largely identical performance on test data as well.
-
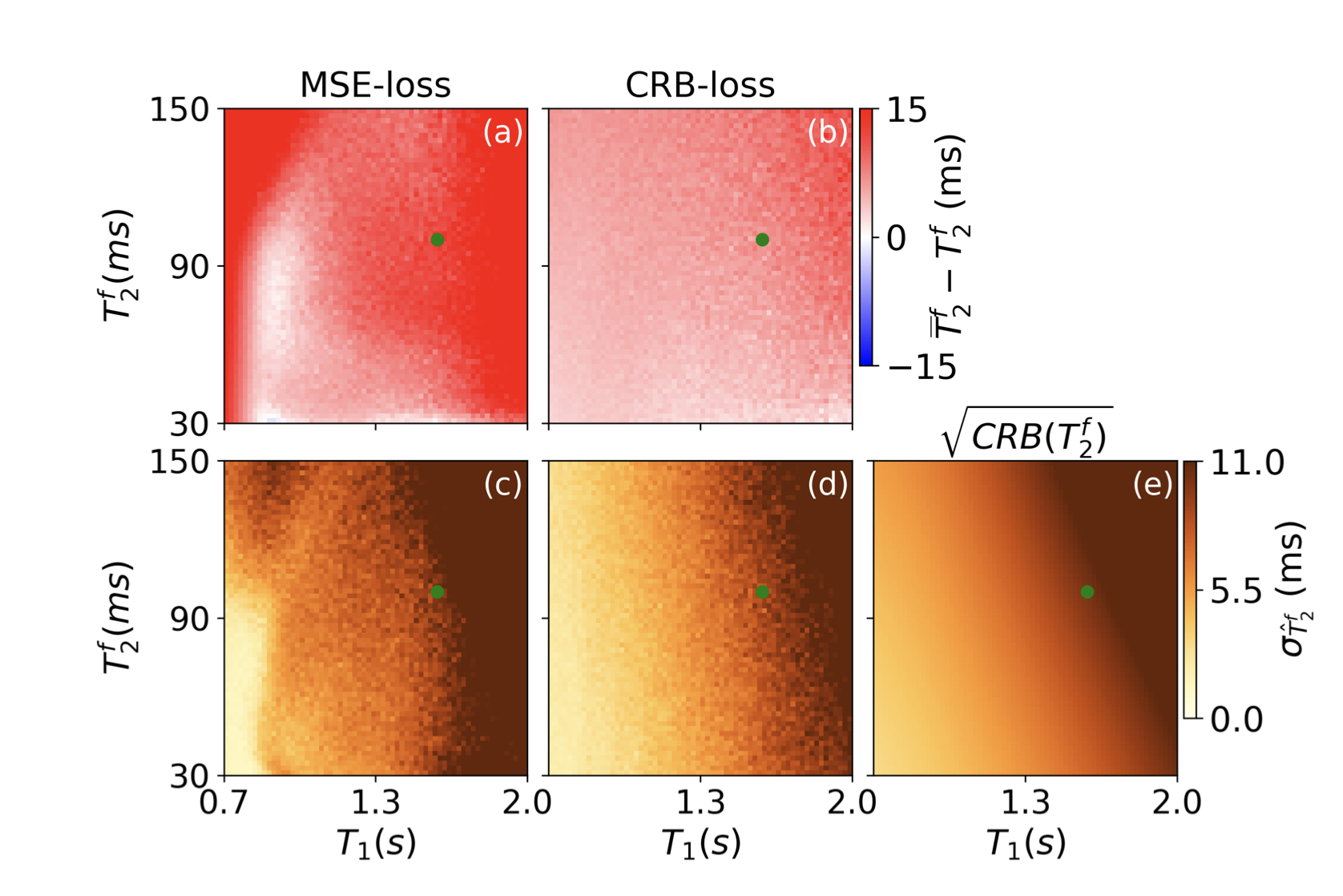
Cramér-Rao bound-informed training of neural networks for quantitative MRI
Xiaoxia Zhang*, Quentin Duchemin*, Kangning Liu* (*Equal contribution), Sebastian Flassbeck, Cem Gultekin, Carlos Fernandez-Granda, Jakob Asslander.
MRM 2021
TL;DR: Theoretically-grounded Cramér-Rao bound loss function for improved neural network MRI parameter estimation.
To address the parameter estimation problem in heterogeneous parameter spaces, we propose a theoretically well-founded loss function based on the Cramér-Rao bound (CRB), which provides a theoretical lower bound for the variance of an unbiased estimator.
-
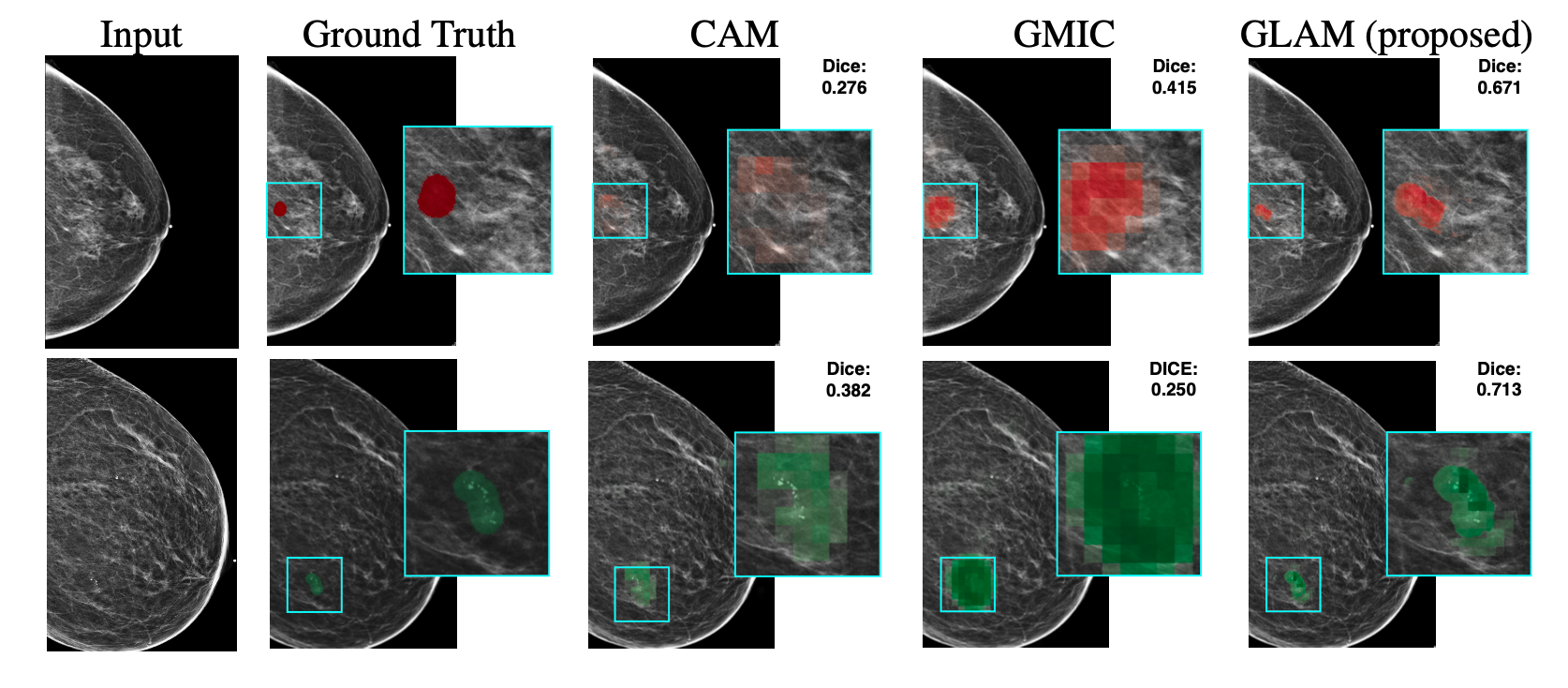
Weakly-supervised High-resolution Segmentation of Mammography Images for Breast Cancer Diagnosis
Kangning Liu, Yiqiu Shen, Nan Wu, Jakub Piotr Chdowski, Carlos Fernandez-Granda, and Krzysztof J. Geras
MIDL 2021
TL;DR: Weakly-supervised segmentation improving breast cancer lesion localization by up to 39.6% over prior methods.
In this study, we unveil a new neural network model for weakly-supervised, high-resolution image segmentation. Focused on breast cancer diagnosis via mammography, our method first identifies regions of interest and then segments them in detail. Validated on a substantial, clinically-relevant dataset, our approach significantly outperforms existing methods, improving lesion localization performance by up to 39.6% and 20.0% for benign and malignant cases, respectively.
-

Unsupervised Multimodal Video-to-Video Translation via Self-Supervised Learning
Kangning Liu*, Shuhang Gu*(*Equal contribution), Andrs Romero, and Radu Timofte
WACV 2021
TL;DR: Unsupervised video translation decoupling style and content for cross-modality conversion with temporal consistency.
In this project, we introduce an unsupervised video-to-video translation model that decouples style and content. Leveraging specialized encoder-decoder and bidirectional RNNs, our model excels in propagating inter-frame details. This architecture enables style-consistent translations and offers a user-friendly interface for cross-modality conversion. We also implement a self-supervised training approach using a novel video interpolation loss that captures sequence-based temporal information.
-
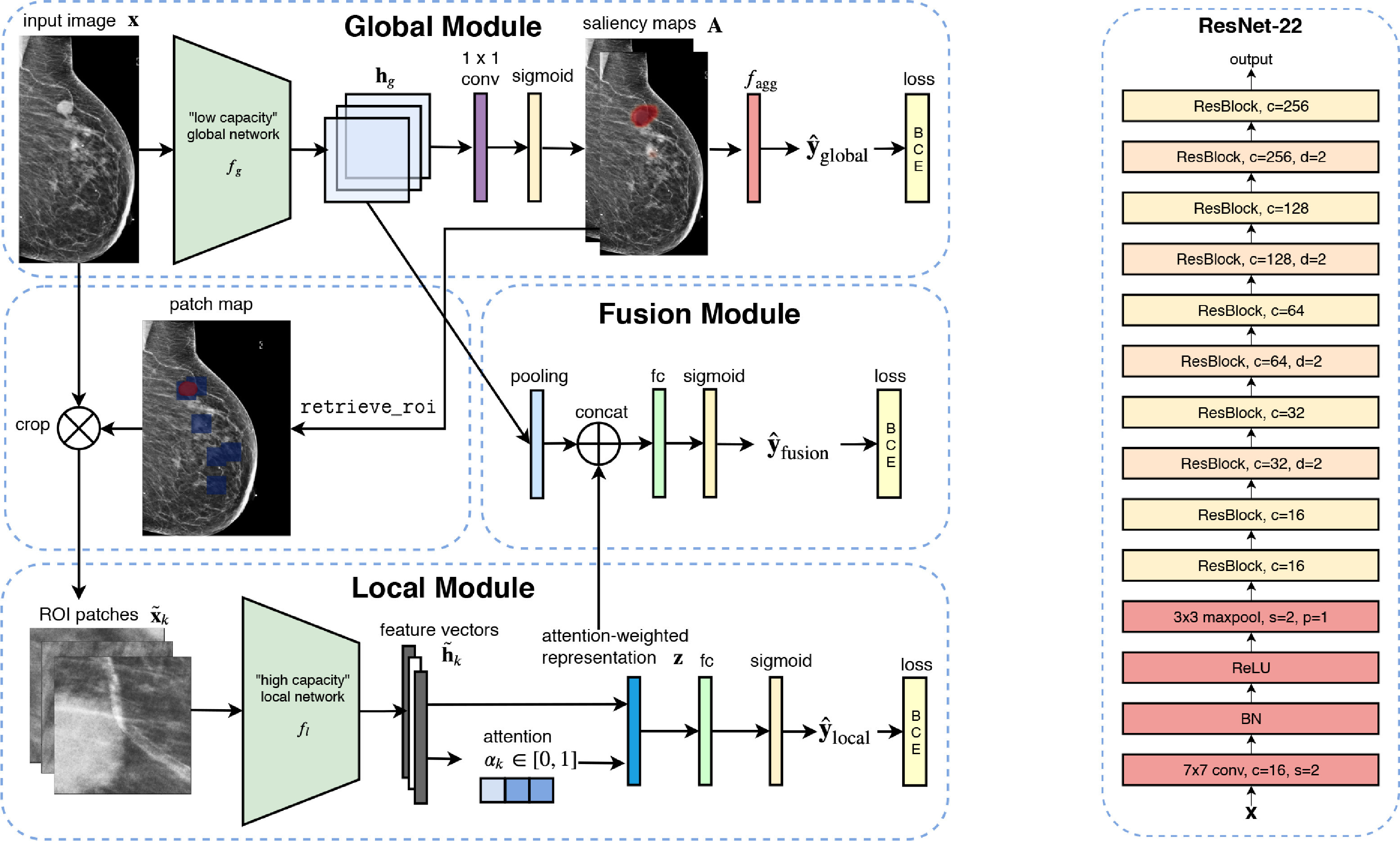
An interpretable classifier for high-resolution breast cancer screening images
Shen, Yiqiu, Nan Wu, Jason Phang, Jungkyu Park, Kangning Liu, Sudarshini Tyagi, Laura Heacock et al.
MedIA 2021
TL;DR: Interpretable neural network for high-resolution breast cancer screening that identifies diagnostically relevant regions.
Medical images differ from natural images in significantly higher resolutions and smaller regions of interest. Because of these differences, neural network architectures that work well for natural images might not be applicable to medical image analysis. In this work, we propose a novel neural network model to address these unique properties of medical images.
Teaching
-
Probability and Statistics for Data Science
NYU, Center for Data Science
Teaching Assistant (Sept - Dec 2021)
-
Advanced Machine Learning
ETH Zurich, Department of Computer Science
Teaching Assistant (Sept - Dec 2018)
Service
-
Awards
- Top Reviewer for NeurIPS 2024
-
Conference Reviewer
CVPR, ICCV, ECCV, NeurIPS, ICLR, ICML, AISTATS, AAAI, WACV
-
Journal Reviewer
TPAMI, TMLR, TNNLS, CVIU
Miscellaneous
-
Capturing moments and exploring light with my Sony A7M4.
Visual Fragments
Pageviews
























